
- Ssh copy file to another server from url how to#
- Ssh copy file to another server from url password#
- Ssh copy file to another server from url download#
Ssh copy file to another server from url how to#
Here are few examples of how to use it for:ġ.
Ssh copy file to another server from url download#
The command won't work unless you correctly enter both passwords.OpenSSH SSH/SecSH protocol suite (which comes pre-installed with OS X and available for download for most other *nix systems) includes the scp (secure copy) application which can be used to upload and download files from and to remote hosts. Scp be prompted to enter two passwords: one for the source system ( ) and one for the destination system ( ). To copy luke.txt from your home directory on to your revenge directory on, enter: txt files from the revenge directory on your account to your revenge directory on, enter:įor the following example, assume you ( dvader) are logged into another computer (that is, some other computer that's not or ). This is necessary because the Unix shell, not the scp command, expands unquoted wildcards. However, to use wildcards for copying multiple source files from a remote system, you need to place quotes ( " ") around the path to the source files.
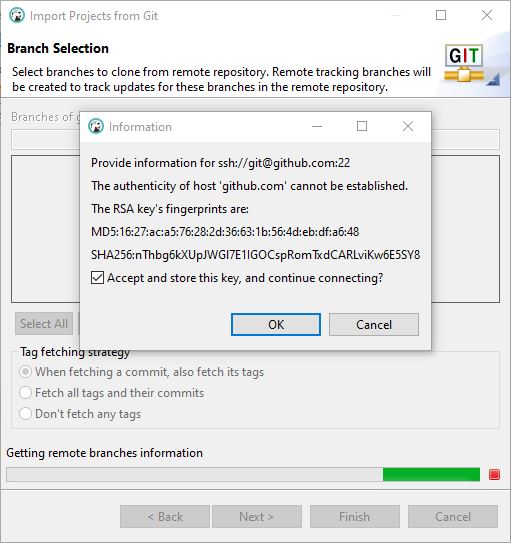
 To copy multiple files within a directory, you can use wildcards (for example, * or ?). The command won't work unless you enter the correct password.
To copy multiple files within a directory, you can use wildcards (for example, * or ?). The command won't work unless you enter the correct password. Ssh copy file to another server from url password#
You'll be prompted for your password on the source system ( ).
To copy the entire revenge directory from your account to your account, enter: This tells scp to recursively copy the source directory and its contents.
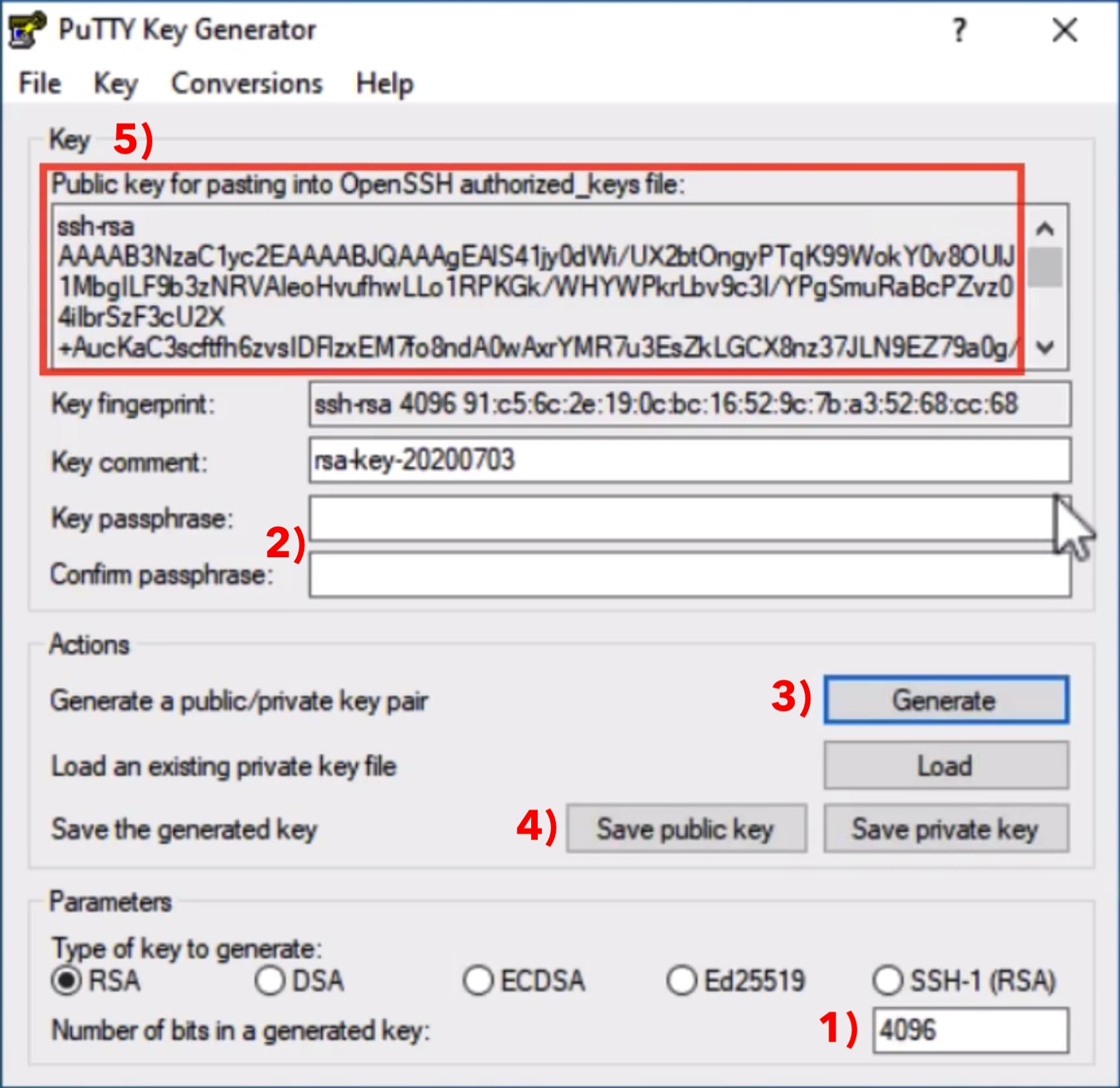
To copy a directory (and all the files it contains), use scp with the -r option. Scp ~/rebels.txt be prompted for your password on the destination system ( ). To copy a file called rebels.txt from your home directory on to a directory called revenge in your account on the computer, enter:. Examplesįor the following examples, assume your username is dvader, and you are logged into your account on the computer : Name of the directory to which the source file will be copied ( directory2)Īt Indiana University, for personal or departmental Linux or Unix systems support, see Get help for Linux or Unix at IU. Hostname of the computer to which the source file will be copied ( destination_host). Name of the account on the destination computer ( username2). The location to which the source file will be copied is specified by which includes the: Filename of the source file ( filename1). Name of the directory containing the source file ( directory1). Hostname of the computer on which the source file resides ( source_host). Name of the account on the host computer ( username1). Scp location of the source file is specified by which includes the: For help, see Get started with Two-Step Login (Duo) at IU and Help for Two-Step Login (Duo). If you have questions about how two-factor authentication may impact your workflows, contact the UITS Research Applications and Deep Learning team. SSH public key authentication remains an option for researchers who submit the "SSH public key authentication to HPS systems" agreement (log into HPC everywhere using your IU username and passphrase), in which you agree to set a passphrase on your private key when you generate your key pair. Two-factor authentication using Two-Step Login (Duo) is required for access to the login nodes on IU research supercomputers, and for SCP and SFTP file transfers to those systems.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
